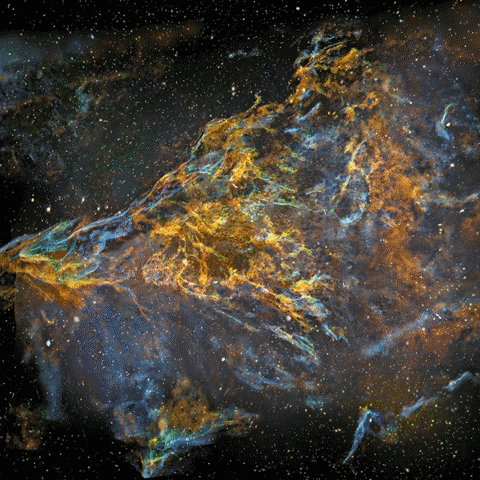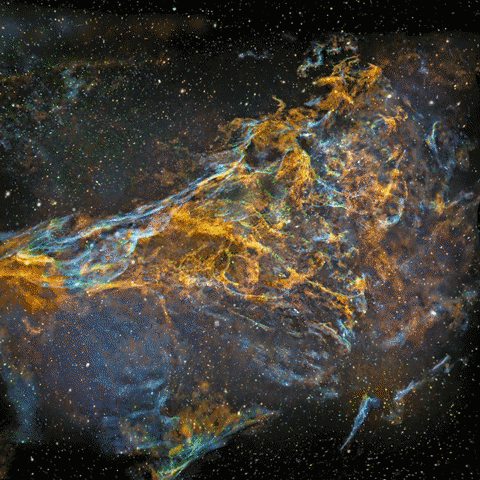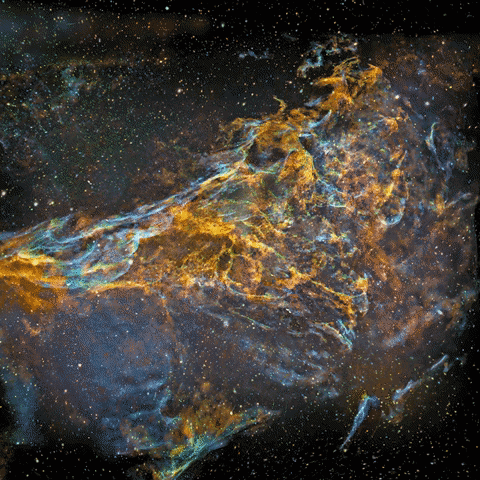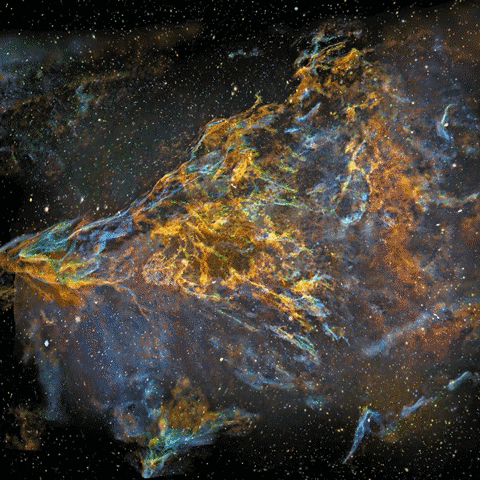COPYRIGHT, PLEASE NOTE
Thursday, September 16, 2021
Viral Nebula Rocks
IC1396 converted to 3D animation, very first of its kind
NOW on SuperRare
I turned my photo of IC1396 to a 3d-model at 2012 to show that it’s actually a three-dimensional volume floating in three-dimensional space. This artwork is not just a guess work, it’s based on scientific data about the structure of emission nebulae and real distance information.
This animation went viral and it was published by several news media and major websites globally at 2012, links after the photos
Original photo used for the animation
My original photo of emission nebula IC1396
PETAPIXEL, Michael Zhang
Amazing Animated GIFs Capture Nebulae in 3D Using Artificial Parallax
https://petapixel.com/2013/02/20/amazing-animated-gifs-capture-nebulae-in-3d-using-artificial-parallax/
This animation was selected to a Moving the Still exhibition in Miami Art Week 2012
How the 3D-model is made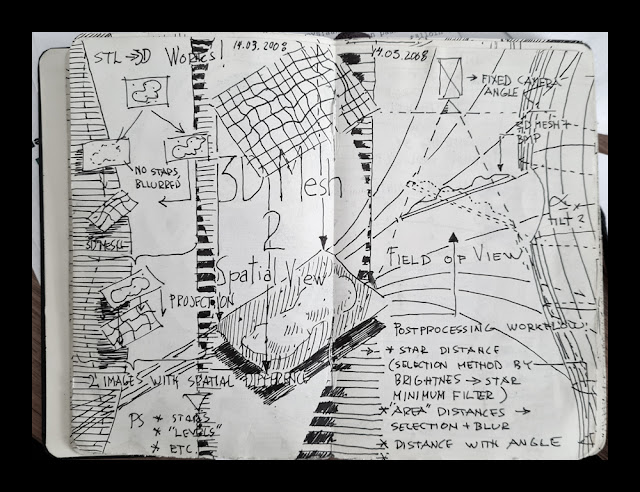 My Moleskine notebook pages from 2008, I planned how to convert nebulae to 3D
My Moleskine notebook pages from 2008, I planned how to convert nebulae to 3D
For as long as I have captured images of celestial objects, I have always seen hem three-dimensionally in my head. The scientific information makes my inner visions much more accurate, and the 3-D technique I have developed enables me to share those beautiful visions with others.
How accurate my 3-D-visions are depending on how much information I have and how well I implement it.
The final 3-D-image is always an appraised simulation of reality based on known scientific facts, deduction, and some artistic creativity.
After I have collected all the necessary scientific information about my target, I start my 3-D conversion from stars. Usually there is a recognizable star cluster which is responsible for ionizing the nebula. We don’t need to know its absolute location since we know its relative location. Stars ionizing the nebula have to be very close to the nebula structure itself. I usually divide up the rest of the stars by their apparent brightness, which can then be used as an indicator of their distances, brighter being closer. If true star distances are available, I use them, but most of the time my rule of thumb is sufficient. By using a scientific estimate of the distance of the Milky Way object, I can locate the correct number of stars in front of it and behind it.
Emission nebulae are not lit up directly by starlight; they are usually way too large for that. Rather, stellar radiation ionizes elements within the gas cloud and the nebula itself is glowing light, the principle is very much the same as in fluorescent tubes. The thickness of the nebula can be estimated from its brightness, since the whole volume of gas is glowing, brighter means thicker.
By this means, forms of the nebula can be turned to a real 3-D shape. Nebulae are also more or less transparent, so we can see both sides of it at the same time, and this makes model-making a little easier since not much is hidden.
The local stellar wind, from the star cluster inside the nebula, shapes the nebula by blowing away the gas around the star cluster. The stellar wind usually forms a kind of cavity in the nebulosity. The same stellar wind also initiates the further collapse of the gas cloud and the birth of the second generation of stars in the nebula. The collapsing gas can resist the stellar wind and produces pillar like formations which must point to a cluster.
Ionized oxygen (O-III) glows with a bluish light, and since oxygen needs a lot of energy to ionize it, this can only be achieved relatively close to the star cluster in the nebula. I use this information to position the O-III area (the bluish glow) at the correct distance relative to the heart of the nebula.
Many other small indicators can be found by carefully studying the image itself. For example, if there is a dark nebula in the image, it must be located in front of the emission one, otherwise we couldn’t see it at all.
Using the known data in this way I build a kind of skeleton model of the nebula. Then the artistic part is mixed with the scientific and logical elements, and after that the rest is very much like creating a sculpture on a cosmic scale
Monday, September 13, 2021
Beyond the astronomical photography
NOTE. Vision series artworks are soon to be sold as NFT @SuperRare
I’m an astrophotographer but first of all I’m a visual artist, as an artist, I’m dazzled by all the forms I’m able to capture in my photos of cosmic objects, nebulae, supernova remnants, galaxies, etc. Colors from ionized elements are connected to the shapes and textures, they form a physical reality around us.
I’m telling a story with my photos, and many times my artworks are also personal notes. The Vision series of photos are forming visual notes about shapes, structures, textures, and colors I have seen and captured during my couple of decades-long journey as an astronomical nature photographer.
Every single element in Vision series photos are from my original astronomical photos. I have been using the Overlapping Lightning Method (Multi Exposure Method) to create my Vision series photographs. By this method the forms and structures in astronomical object get multiplied, they are now forming a new visual dimension beyond our physical universe.
The photographic method I'm using was fashionable back in the 1920s among avant-gardists and surrealistic photographers. At the time the work was done in a darkroom, I’m using about the same technique but instead of a darkroom, I’m using digital image processing.
The original photo is rotated, moved, and/or mirrored as I like, and then multiple layers stacked back together so that the original brightness is maintained. For this task, I use Photoshop and various astronomical stacking methods and applications.
Few samples of my Vision Series, the original astronomical photo I used to create them at end of the page.
Visions of Veil
Please, click for a large image
Visions of Veil series is based on my original photo
Friday, August 27, 2021
Visions of Veil
This is an experimental test with a 3D-conversion of my astronomical image. Only real elements from the original image are used, there is nothing added but the estimated volumetric information!
NOTE. This is a personal vision about shapes and volumes, based on some scientific data, deduction and an artistic impression.Tuesday, August 17, 2021
A starless Pickering's Triange
As far as I know, I was the first who published starless nebula images back in 2007. At the time the feedback was less than positive.
The reason to publish such a unorthodox images was that the starless version is a part of my processing workflow and it can sometimes show more than the actual image.
I have used this technique ever since and published some starless images now and then.
Starless images are very powerful, when I want to dig out some really dim objects in a very dense starfield. It makes processing so much easier, I don't need to be careful not to blow up the stars.
Normally all the stars are placed back with a zero data lost after processing is done.
Starless images are also a great help to see the actual structure in the nebula since human brains has a tendency to form a quasi logical shapes out of the random cloud of dots, like stars are.
Please, click for a large image, it's worth it!
https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2015/09/pickerings-triangle-my-first-light-for.html
Monday, August 9, 2021
Pickering's Triangle reprocessed with some new data
I originally shot this image at September 2015 and it was selected as a NASA APOD (Astronomy Picture of the Day) at same month.
I kind of like the result, colors are more vivid and background has deeper shades.
Please, click for a large image, it's worth it!
Colors are from the ionized elements, Hydrogen, Sulfur and Oxygen.
S-II = Red, H-alpha = Green and O-III = Blue.
Technical details and more images:
https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2015/09/pickerings-triangle-my-first-light-for.html
Sunday, August 1, 2021
A new photo, Monkey Head Nebula, Lower's nebula, Jelly Fish nebula and Messier 35
I shot material for this mosaic image at end of the spring season 2021. I haven't got time to finalize it until now. I kind of like this image, it's very deep and shows the very dim background mist and a very dense starfield of the galaxy plane. Total exposure time with Tokina AT-x 300mm f2,8 camera lens, Apogee u16 Astro camera and Astrodon narrowband filters is around 6 hours, the exposure time with Celestron Edge telescope is around 30 hours.
An other interesting feature in this imaging project is that I did use my VARES-processing method to this.
(Variable Resolution imaging) I have shot the nebulae in this wide field image with a long focal length instrument, the Celestron Edge 11" few years ago. I use this high res material to boost details in the wide field image. But that's not all!
I used the VARES technique to add deepness to my older long focal length images. I added the very dim background nebula data from wide filled images to long focal length images. The result was very good. Now all detailed features in the image, like stars, brighter nebula details and dark nebulae are form high res image data. The dim and relatively featureless data is taken from the wide field image. At the end the both datasets are combined by VARES-processing method to a one very deep and detailed image.
Click for a large image!
Monkey Head nebula, NGC 2175
Click for a large image
The wide field data boosted long focal length image, original photo and details can be seen here, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2015/03/ngc-2174-monkey-head-nebula-project.html
I think, this was a first image in the World showing the extremely dim lower part, "Teil of the Monkey", of the nebula.
Click for a large image
Click for a large image
Monday, July 19, 2021
Voices of Apollo 11
@FORBES
are now part of the Moon forever
This is also a tribute to the entire Apollo 11 team: Commander Neil A. Armstrong, Command Module Pilot Michael Collins, and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
I was most gratified and deeply moved when Michael Collins —the Apollo 11 & Gemini 10 astronaut, author, explorer and artist— tweeted following kind words about my work on April 19th, 2021: https://twitter.com/AstroMCollins/status/1384194949009211393
The news of his passing, just nine days later, hit me all the harder — a very emotional moment for me. Out of the blue, I got inspired to create this artwork. I absolutely had to do it right away, which I did.
Michael Collins was affectionately referred to as “the loneliest man in history” for being the command module pilot who flew solo in space behind the Moon and without radio contact with anyone while his colleagues, Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong, set foot on the Moon for the first time in history. Michael was also an artist. His iconic photos made from Moon orbit are true art and part of mankind's greatest cultural heritage treasure.
A similar solitude gripped me while I was creating this tribute image. For being an astronomical photographer and a visual artist often is a very lonely job. Especially this time as I was deeply emotional throughout my creative process for this artwork. Even though I never met him personally, the end of his Earthly mission meant more to me than I was prepared for. I needed to make this photo-based artwork to process the inner storm of my thoughts and feelings.
Click for a larger image.
Wednesday, June 23, 2021
Photo number 8, The Chinese Dragon
Duration ~one minute
When you spent a decade working with a one photo to get it ready, it's like a long marriage. The passionate love is slowly turning to a deeper connection and at the end you'll grow together and can't live without the others company. As in marriage, during the years I have had friction in the relationship, even hate. But after desperate times the love always wins.
I'm a perfectionist, when dealing with my photography. This feature is essential for a great results but it also can cause problems in relationship. There have been times when I almost get a divorce and started looking for another, easier target since I couldn't get out all of the extreme dim and difficult details I wanted to see and show. I didn't even know, if they are there since there wasn't any references to compare. I didn't give up and finally after long nights and hundreds of exposure hours I get what I was after. Now we can grow old together and I know for sure, I will always find something new and existing from my love one, the Chinese Dragon..
I have started this imaging project back at 2010. My aim was to make a high resolution mosaic covering the whole constellation Cygnus. Work like that takes time and patience, especially since I have worked so, that many of the individual sub mosaics or frames can be published as an individual artworks. Here is a poster format presentation about all of the longer focal length images used for this mosaic beside longer focal length panels.
As a result I have now a huge 95 panel mosaic panorama covering 28 x 18 degrees of sky. I have collected photons way over 600 hours during past ten years for this photo. The full size mosaic image has a size of about 25.000 x 15.000 pixels.
Just outside of the field of view lays the famous Veil Nebula SNR at bottom middle.
Beside two supernova remnants there are two Wolf Rayet stars with outer shell formations. NGC 6888, the Crescent Nebula at center of the image and the WR 134, it can be seen as a blue arch just right from the Crescent Nebula, near the Tulip nebula.
Next to the Tulip Nebula lays a Black hole Cygnus X-1.
Constellation Cygnus is an endless source of celestial wonders, both scientifically and aesthetically. For me, as an visual artist, this area of night sky is very inspiring There are endless amount of amazing shapes and structures, I can spend rest of my life just shooting images from this treasury.
Original resolution in pixels, 25.000 x 15.000
The NASA astronomer wrote about this image:
I have used several optical configurations for this mosaic image during the years. Up to 2014 I was using an old Meade LX200 GPS 12" scope, QHY9 astrocam, Canon EF 200mm f1.8 camera optics and baader narrowband filter set.
After 2014 I have had 10-micron 1000 equatorial mount, Apogee Alta U16 astro camera, Tokina AT-x 200mm f2.8 camera lens and the Astrodon 50mm square narrowband filter set.
I have shot many details with a longer focal length, before 2014 by using Meade 12" scope with reducer and after 2014 Celestron EDGE 11" and reducer. Quider camera has been Lodestar and Lodestar II.
A version of this photo was selected as an Astronomical Picture Of the Day by NASA
Here is a poster format presentation and a list all of longer focal length images used for this mosaic beside the actual panels, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2018/11/treasures-of-swan.html
Click for a large image
Friday, May 7, 2021
All my photos from the Spring season 2021
Click for a large image
- "The Space Between Us" https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/03/space-between-cygnus-and-cepheus.html
- The Constellation cassiopeia
- From Cassiopeia to Cygnus, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/02/this-gigapixel-mosaic-has-over-900.html
- "Cirrus of Cygnus", https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2020/12/cirrus-of-cygnus-and-supernova-remnant.html
- SNR G65.5+5.7, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2020/11/g65357-large-supernova-remnant-in_22.html
- Sharpless 132, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/02/sharpless-132-sh2-132-with-new-data.html
- Lower's Nebula, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/01/lowers-nebula.html
- From Taurus to Perseus, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/02/a-new-mosaic-image-from-taurus-to.html
- From Cassiopeia to Cepheus, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/01/mosaic-image-gets-large-400-hours-and.html
- From Cassiopeia to Cepheus, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/01/mosaic-image-gets-large-400-hours-and.html
- The Grand Mosaic of the Milky Way, https://astroanarchy.blogspot.com/2021/03/gigapixel-mosaic-of-milky-way-1250.html
All my photos from the year 2020
Click for a full size poster (2000 x 2800 pixels)
That's me in the silhuet. The image can be seen some kind of planetary conjunction or even a stylished Moon. But it actually shows a very typical situation when I'm about to start an imaging session and I'm looking for the sky quality. The half circle like cutting at two o'clock is showing the rear end of my telescope.
Thursday, May 6, 2021
4K videos about the Grand Mosaic of the Milky Way
The only photo in the World showing the Northern Milky Way in this accuracy and depth.
Original photo has so high resolution, that's impossible to show over the web, I made those videos to bring out even some of the accuracy of the original photo.
Please, use a 4K-display or the TV-set to watch the video, if possible.
It does play nicely in normal HD-display but you'll get much more out of this by using the 4K-display.
4K-VIDEO 2
Panoramic photo of the Northern Milky Way
Monday, March 22, 2021
A temporary WEB SHOP OPENED
This is a very temporary Web Shop and I'll shut it down in near future!
You can now buy my photos as a photographic prints
Please, have a look, https://astroanarchy.zenfolio.com/
Sunday, March 14, 2021
Space between Cygnus and cepheus
I have published several large mosaic image panoramas in a past year. I have made several smaller sub-panoramas, they are working as an independent artworks.
This image shows an area between well known and much imaged objects, I always like to find a new viewpoints to the sky.
The space between Cygnus and Cepheus
Click for a large image, it's worth it
Click for a large image,
The mosaic, technical info
Thursday, March 4, 2021
Nebulae of Auriga and how my mosaic images are done.
I'll like to show the actual resolution of this and other of my large mosaic images by posting a close up from this panorama. Since there are data from so many years (2009 -2021) and it has been shot with various optical configurations, I had to develop a new method to combine frames for a mosaic image.
Click for a large image
Up to 2014 I was using an old Meade LX200 GPS 12" scope, QHY9 astrocam, Canon EF 200mm f1.8 camera optics and baader narrowband filter set. After 2014 I have had 10-micron 1000 equatorial mount, Apogee Alta U16 astro camera, Tokina AT-x 200mm f2.8 camera lens and the Astrodon 50mm square narrowband filter set. I have shot many details with a longer focal length, before 2014 by using Meade 12" scope with reducer and after 2014 Celestron EDGE 11" and reducer. Quider camera has been Lodestar and Lodestar II.
I took my current toolset as a base tool since it has a relatively high resolution combined to a very large field of view. Also it collects photons very quickly since it's undersampled and I can have very dim background nebulosity visible in very short time (many times 30 min frame is enough)
I do all my mosaic work under the PhotoShop, Matching the separate panels by using stars as an indicator is kind of straight forward work. My processing has become so constant, that very little tweaking is needed between separate frames, just some minor levels, curves and color balance.
I have used lots of longer focal length frames in my mosaic to boost details. To match them with shorter focal length shots I developed a new method.
Firstly I upscale the short focal length frames about 25% to have more room for high resolution images.Then I match the high res photo to a mosaic by using the stars as an indicator. After that I remove all the tiny stars from the high res image. Next I separate stars from low res photo and merge the starless high res data to a starless low res frame. And finally I place the removed low res stars back at top of everything with zero data lost. Usually there are some optical distortions and it's seen especially in a star field. Now all my stars are coming from a same optical setup and I don't have any problems with distortions. (I'm using the same star removal technique as in my Tone Mapping Work Flow)