COPYRIGHT, PLEASE NOTE
All the material on this website is copyrighted to J-P Metsavainio, if not otherwise stated. Any content on this website may not be reproduced without the author’s permission.
BUY A MUSEUM QUALITY POSTER
BUY A POSTER:https://astroanarchy.zenfolio.com/
Monday, October 4, 2021
Three 3D-conversions out of my astronomical photos
I have made dozens of 3D-conversions out of my astronomical photos. As an artist I like to find a new views to the reality. My models are not just a guesswork, the conversion is based on real scientific data.
At the end of this blog post there is a short explanation, how I do my conversion work.
Veil nebula in O-III light alone
Original astronomical photo about part of the Veil nebula SNR in O-III light only.
Original astronomical photo about part of the Veil nebula SNR in O-III light only.
3D-study of Veil Nebula Photo
NGC1499 the California Nebula
My photo of California Nebyla in mapped colors
3D-study of California Nebula Photo
Bubble Nebula
3D-study of Bubble Nebula Photo
How 3D-models are made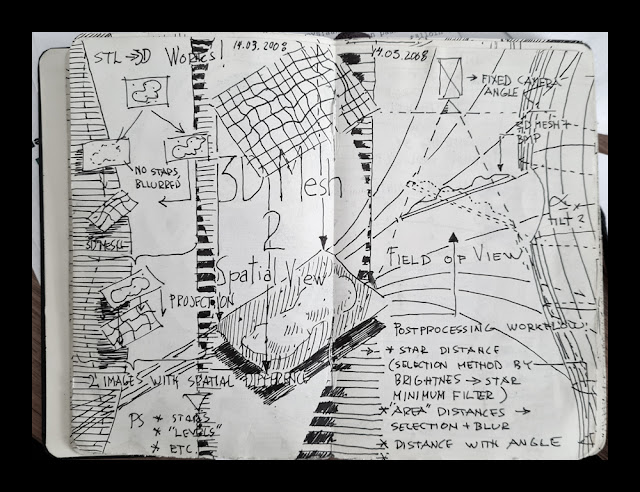 My Moleskine notebook pages from 2008, I planned how to convert nebulae to 3D
My Moleskine notebook pages from 2008, I planned how to convert nebulae to 3D
How accurate my 3-D-visions are depending on how much information I have and how well I implement it.
The final 3-D-image is always an appraised simulation of reality based on known scientific facts, deduction, and some artistic creativity.
After I have collected all the necessary scientific information about my target, I start my 3-D conversion from stars. Usually there is a recognizable star cluster which is responsible for ionizing the nebula. We don’t need to know its absolute location since we know its relative location. Stars ionizing the nebula have to be very close to the nebula structure itself. I usually divide up the rest of the stars by their apparent brightness, which can then be used as an indicator of their distances, brighter being closer. If true star distances are available, I use them, but most of the time my rule of thumb is sufficient. By using a scientific estimate of the distance of the Milky Way object, I can locate the correct number of stars in front of it and behind it.
Emission nebulae are not lit up directly by starlight; they are usually way too large for that. Rather, stellar radiation ionizes elements within the gas cloud and the nebula itself is glowing light, the principle is very much the same as in fluorescent tubes. The thickness of the nebula can be estimated from its brightness, since the whole volume of gas is glowing, brighter means thicker.
By this means, forms of the nebula can be turned to a real 3-D shape. Nebulae are also more or less transparent, so we can see both sides of it at the same time, and this makes model-making a little easier since not much is hidden.
The local stellar wind, from the star cluster inside the nebula, shapes the nebula by blowing away the gas around the star cluster. The stellar wind usually forms a kind of cavity in the nebulosity. The same stellar wind also initiates the further collapse of the gas cloud and the birth of the second generation of stars in the nebula. The collapsing gas can resist the stellar wind and produces pillar like formations which must point to a cluster.
Ionized oxygen (O-III) glows with a bluish light, and since oxygen needs a lot of energy to ionize it, this can only be achieved relatively close to the star cluster in the nebula. I use this information to position the O-III area (the bluish glow) at the correct distance relative to the heart of the nebula.
Many other small indicators can be found by carefully studying the image itself. For example, if there is a dark nebula in the image, it must be located in front of the emission one, otherwise we couldn’t see it at all.
Using the known data in this way I build a kind of skeleton model of the nebula. Then the artistic part is mixed with the scientific and logical elements, and after that the rest is very much like creating a sculpture on a cosmic scale
Labels:
animations,
Narrowband color images,
nebula
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)













No comments:
Post a Comment